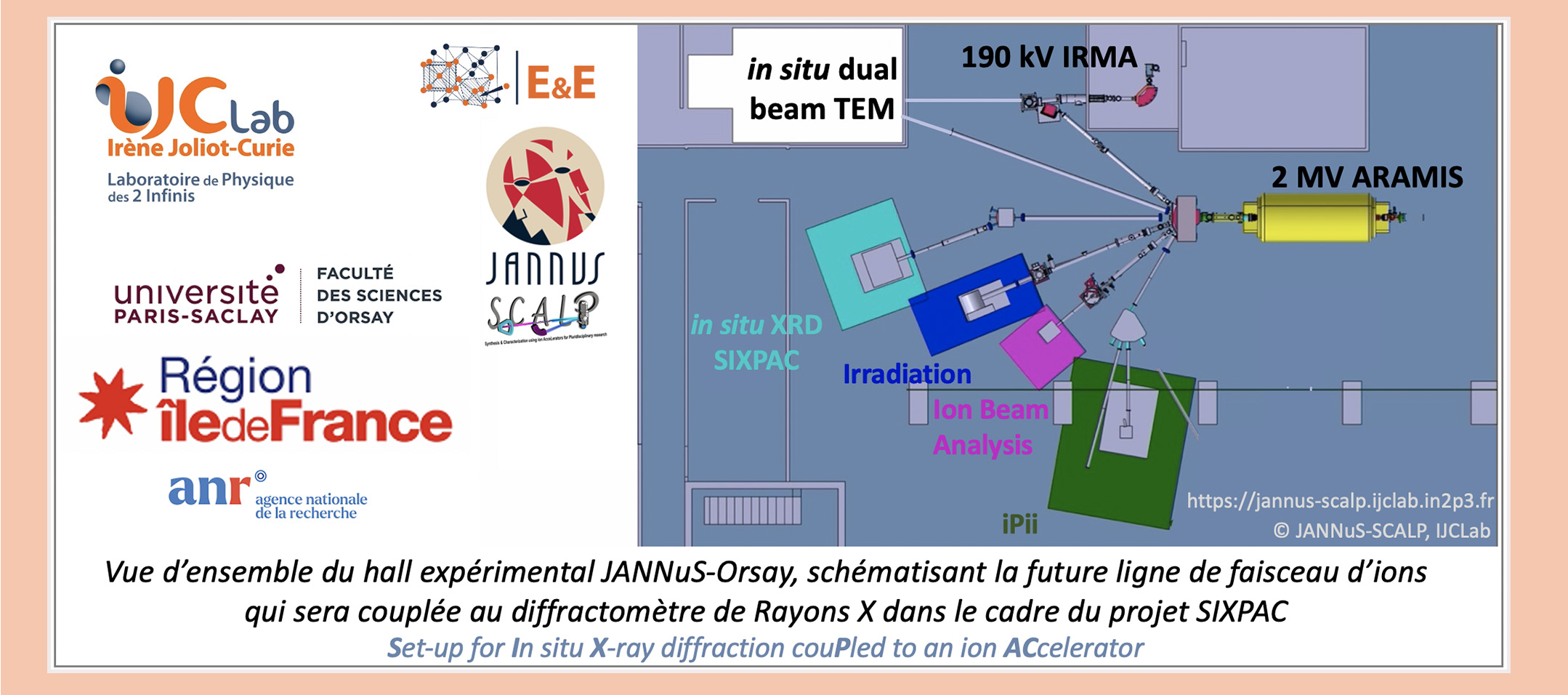
The SIXPAC project (Set-up for In situ X-ray diffraction couPled to an ion Accelerator), led by the Energy & Environment Pole and the JANNuS-SCALP platform of IJCLab, has just been selected by the Ile-de- France within the framework of the SESAME 2022 call: this funding will complement those of Université Paris-Saclay (ERM 2021), ANR CIRANO 2022 and IJCLab, and will allow the construction of a new beamline of ions from the ARAMIS accelerator of the JANNuS-SCALP platform, connected to a high-performance X-ray diffractometer.
This new state-of-the-art equipment, unique in the world, will make it possible to monitor in situ the (micro-) structural modifications induced by ion irradiation in a material, in the energy range of a few hundred keV to a few MeV. It will make it possible to study in situ the microstructural evolution of materials subjected to irradiation, such as those envisaged for the nuclear industry of the future (fission and fusion). This project, led by IJCLab, in close partnership with the SRMP (CEA Saclay, ISAS), will strengthen the experimental possibilities offered by JANNuS-Orsay and Saclay, linked by a Scientific Interest Group.
The experimental characterization techniques conducted in situ, coupled with ion beams delivered by an accelerator, allow the description of all the phenomena involved during irradiations, undergone by the materials or used to control the physico-chemical modifications. resulting from this process outside of thermodynamic equilibrium. X-ray diffraction, a non-destructive characterization technique used in the new SIXPAC experimental device, will complete the platform's offer (in situ transmission electron microscopy with two ion beams, in situ RBS-C), allowing in particular the measurement of the elastic deformation, and the access to the first stages of the damage of materials under irradiation.
To know more on Energy & Environment Pole.